뇌 전이 소견을 보인 췌장암: 증례보고 및 문헌고찰
Pancreatic Cancer with Brain Metastases: Case Report with Literature Review
Article information
Abstract
췌장암에서 유래된 뇌 전이는 매우 드물며, 뇌 전이가 동반된 췌장암 환자의 예후는 매우 나쁜 것으로 알려져 있다. 뇌 전이의 수술적 절제는 도움이 되나 제한적이며, 원발 췌장암이 조절되고 있는 환자에서 장기 생존이 가능하다. 저자들은 유문 보존 췌십이지장 절제술 후 간 전이에 대한 화학 요법의 완전 반응을 보인 췌장암 환자에서 새로 발생한 뇌 전이를 경험하였기에 문헌고찰과 함께 보고한다. 이 환자는 뇌 전이 병소가 성공적으로 절제되고, 췌장암에 대한 근치적 치료를 받았음에도 불구하고 상대적으로 생존 기간이 짧았다. 이 증례는 조절되고 있는 췌장암에서 유래된 뇌 전이 병소의 절제가 도움이 될 수 있지만, 그 절제 시기도 중요하다는 것을 알려주고 있다.
Trans Abstract
Pancreatic cancer is well known as a relentlessly progressive and fatal disease. Although distant metastasis is common at the time of diagnosis, brain metastasis originating from pancreatic cancer is rare and its clinical manifestation remains poorly described. Additionally, it is generally known that the prognosis for patients with pancreatic cancer and brain metastasis is very poor. Surgical resection of brain metastasis may play a limited role or may allow long-term survival in patients for whom the primary pancreatic cancer is well controlled. We present a case of brain metastasis in patient with pancreatic cancer after pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy and complete response to chemotherapy for hepatic metastases. Brain metastasis was resected successfully, but survival period was relatively short, even though the patient received curative treatment for pancreatic cancer. This case demonstrated that resection of brain metastatic lesion from pancreatic cancer being controlled may be helpful, but the timing of resection is also important.
INTRODUCTION
Most brain metastases arise from three major malignancies: lung cancer, breast cancer, and malignant melanoma [1]. Brain metastases originating from gastrointestinal cancer are extremely rare. The incidence of brain metastasis from gastric cancer is below 1% and that from colorectal cancer is approximately 4% [2-4]. Metastases to the brain and central nervous system are very rare from pancreatic cancer; only about 0.33% of pancreatic cancers metastasize to the brain [5].
In this report, we present a case of resected pancreatic cancer with brain metastasis after long-term remission. We also systematically reviewed published articles on brain metastases originating from pancreatic cancer, which focused on patient characteristics, clinical appearance, management, and outcomes.
CASE
In May 2012, a 52-year-old woman presented with a week-long history of jaundice. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed a 4.0 cm low-density mass at the head of the pancreas, which invaded the duodenum (Fig. 1A). Endoscopically, an ulcerofungating mass lesion was identified in the second portion of the duodenum, and a biopsy of the lesion revealed metastatic adenocarcinoma from the pancreas. Laboratory tests showed the following: bilirubin (total/direct), 12.0/8.0 mg/dL; aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase, 168/315 U/L; alkaline phosphatase, 518 U/L; and gamma glutamyl transpeptidase, 632 U/L. The carbohydrate antigen 19–9 (CA 19–9) level was 2,758 U/mL.
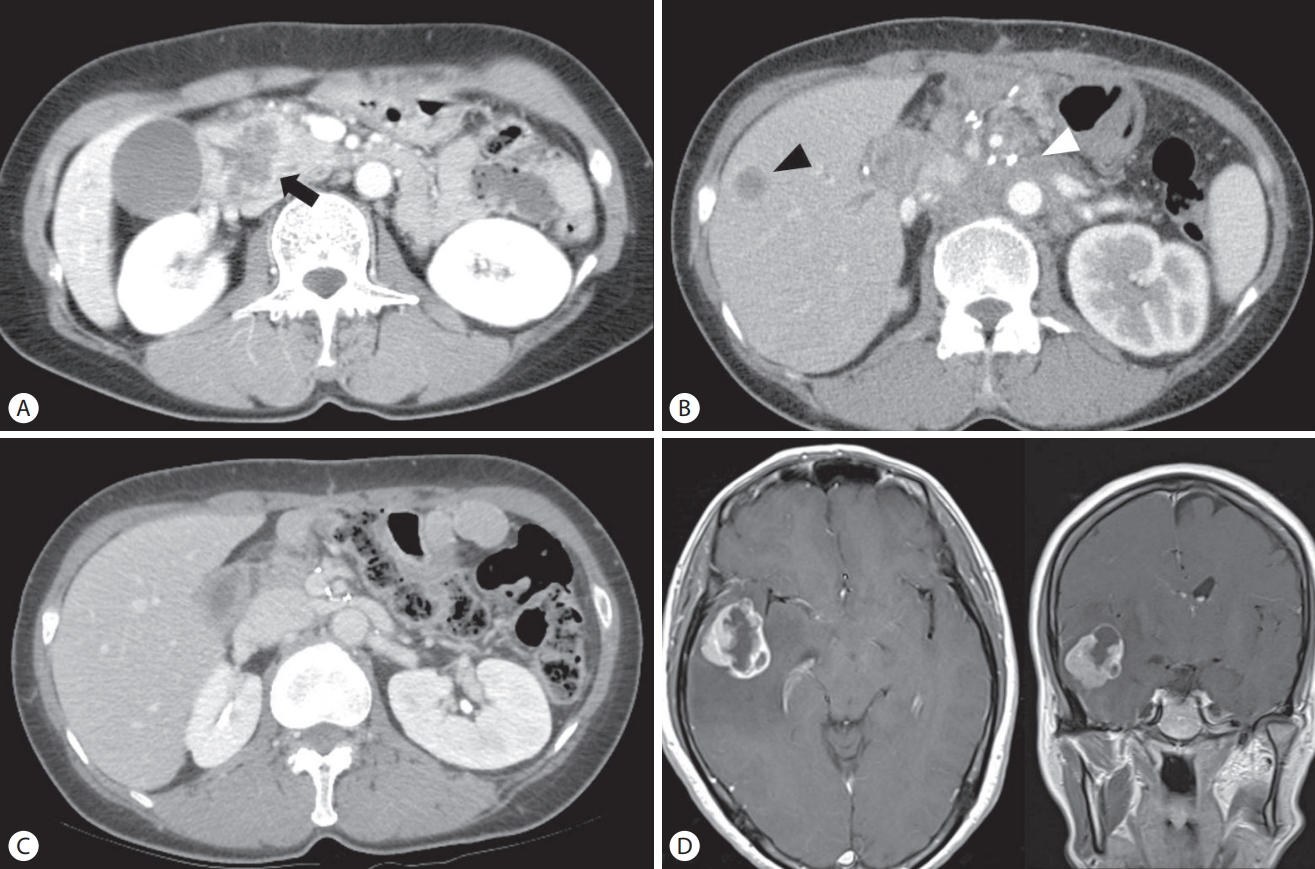
Images of computed tomography (CT) and magnet resonance image. (A) Initial abdominal CT showed approximately 4.5 cm sized, rim enhancing low density mass (black arrow) in the head of pancreas, suggesting pancreatic head cancer. (B) Three months after pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy, follow-up CT revealed a 1.5 cm newly appeared hepatic metastasis in the segment 5 (black arrowhead) and multiple metastatic lymphadenopathies (white arrowhead) around abdominal aorta. (C) After chemotherapy using cisplatin and capecitabine, hepatic metastasis and multiple metastatic lymph nodes were disappeared. (D) Contrast enhanced T1-weighted axial and coronal image showed approximately 4 cm sized, irregular thick walled enhancing mass with extensive surrounding edema in right temporal lobe, suggesting brain metastasis.
After excluding distant metastasis using positron emission tomography, the patient underwent pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy. The pathologic result of the operation revealed a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with lymph node metastases, and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC, 7th edition) stage was IIB. Thereafter, the patient received a total of three cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy (gemcitabine, 1,000 mg/m2 weekly for the first 3 weeks and then 1 week of rest). Follow-up abdominal CT revealed multiple new hepatic metastases (Fig. 1B), and secondary chemotherapy was administered using the XP regimen (capecitabine 1,000 mg/m2 twice daily on days 1–14, and cisplatin 60 mg/m2 on day 1, every 3 weeks) from October 2012 for a total of eight cycles to March 2013. A partial response based on the Revised Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) criteria was attained. Since April 2013, she was treated with only capecitabine (1,000 mg/m2 twice daily on days 1–14, every 3 weeks) because of emesis caused by cisplatin and poor performance status, and she had received a total of 11 cycles until October 2013. Follow-up abdominal CT revealed disappearance of all metastatic lesions in the liver (Fig. 1C).
In November 2013, she complained of a headache and transient paresthesia in the left leg. Although abdominal CT, which was performed 1 week prior to the presentation, indicated that she had achieved complete response, CA 19-9 level was elevated to 99.7 U/mL, compared to 13.3 U/mL detected 2 months prior. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a 3.3 cm mass in the right temporal lobe (Fig. 1D). After 1 month, she was referred to the emergency department with headache, dizziness, and vomiting. She underwent a craniotomy and resection of the temporal lobe mass. Histological examination of the brain specimen revealed a metastatic adenocarcinoma (Fig. 2A, B), which was consistent with the primary pancreatic tumor based on immunohistochemical staining (Fig. 2C, D). Follow-up brain MRI showed small new metastases in the right frontal base and right occipital lobe, and she underwent gamma knife surgery in January 2014. Despite aggressive treatment, the neurological symptoms progressed and the patient died in April 2014.

Histologic and immunohistochemical findings of the brain biopsy. (A) Histological section shows abortive tubular structures or cell clusters and deeply infiltrative growth pattern. (hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×100). (B) High power view shows solid nests and poorly formed glands, composed of columnar to cuboidal epithelial cells with eosinophilic and granular cytoplasm (hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×200). The malignant glandular cells show diffuse strong immunohistochemical reactivity for cytokeratin (CK) 7 (C, ×100) and CK 19 (D, ×100).
DISCUSSION
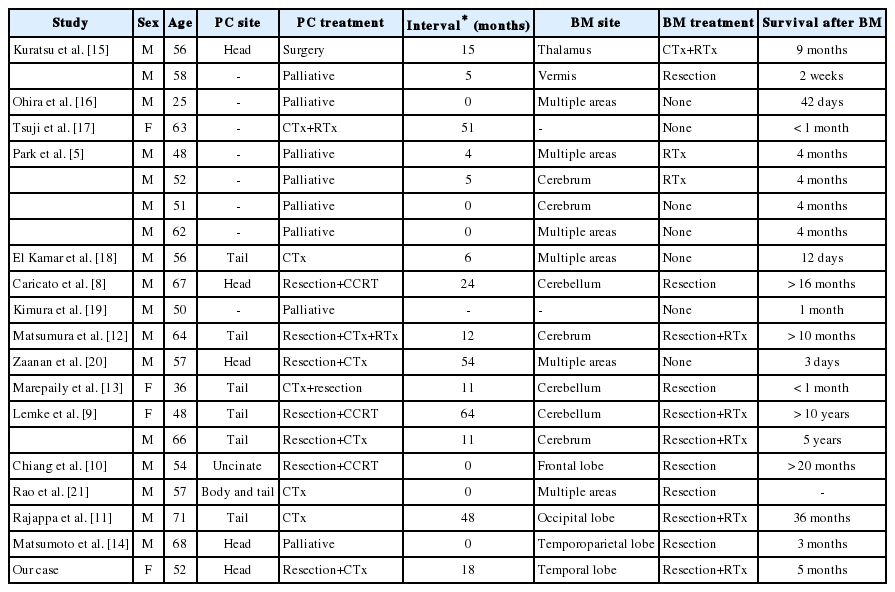
Brain metastases are frequently diagnosed in patients with lung cancer (48%), breast cancer (15%), testicular cancer (10% to 15%), and malignant melanoma (6% to 10%). However, they rarely arise from gastrointestinal tract cancers [6]. Brain metastases are reported in < 4% of malignancies affecting the esophagus, stomach, colon, and rectum [7]. Brain metastases originating from pancreatic cancer are exceedingly rare, which have been reported in 0.33% of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cases [5]. This is attributed to the aggressive nature of pancreatic adenocarcinoma and the fact that most patients do not exhibit sufficiently long survival periods for tumor cells to invade the nervous system [5,8]. To the best of our knowledge, only 21 cases of brain metastases from pancreatic cancer identified antemortem have been reported to date, including our case. Table 1 summarizes the clinical features of these cases. Most patients have been men (17 men, 4 women), and brain metastases represented the first manifestation of pancreatic cancer in 6 patients. Prognosis was extremely poor, with the majority of patients dying within a year, most of them within weeks or months. Four patients survived for longer than 20 months, 36 months, 6 years, and 10 years, respectively, after the diagnosis of brain metastases [9-11].
In general, the treatment strategy for brain metastases from pancreatic cancer tends to be palliative due to the extremely poor prognosis. Treatments for metastatic brain tumors from pancreatic cancer have included surgical resection, whole-brain radiotherapy and stereotactic radiosurgery [8-15]. Given the radio-resistant nature of most pancreatic cancers, radiotherapy appears to offer little benefit [5,6]. In contrast, aggressive surgical resection may prove to be effective. Ten reports have described surgical resection for metastatic brain tumors from pancreatic cancer, including our case [8-15]. Survival periods were significantly longer in patients who underwent surgical resection than in patients who did not undergo resection.
In contrast to our case, Lemke et al. [9] reported two patients with long-term survival of more than 5 years after surgical resection. Based on a literature review of favorable survival in patients with brain metastases, curative therapy for pancreatic cancer was associated with long-term survival after a diagnosis of brain metastasis [14]. However, in our case, the survival period was relatively short (5 months), even though the patient received curative treatment for pancreatic cancer. This may be related to the fact that the patient refused treatment for brain metastasis at the time of its diagnosis, and that she was treated only after the symptoms deteriorated 1 month later. Although she had undergone resection for brain metastasis 1 month after the diagnosis, additional brain metastases were confirmed on postoperative imaging, suggesting that the timing of resection for brain metastasis was delayed.
In conclusion, we reported a case of brain metastasis from pancreatic cancer that showed favorable progress with palliative chemotherapy for 13 months. Brain metastasis should be considered in patients with pancreatic cancer presenting with new neurological symptoms.
Although the prognosis for patients with pancreatic cancer and brain metastasis is very poor, surgical resection of brain metastasis may allow for long-term survival in patients in whom the primary pancreatic cancer is well controlled. Therefore, surgical resection of brain metastases at the appropriate time may improve patient prognosis.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.