췌장담도 질환에서 진단 인공지능 응용
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis of Pancreaticobiliary Diseases
Article information
서론
인공지능(artificial intelligence, AI)이 급속도로 현대 기술에 적용되면서 의료 분야에서도 그 활용도와 응용에 대해 많은 연구가 되고 있다. 실제 임상에서 AI 기술은 영상 해석 능력, 정확성을 증가시키며, 가상 프로그램으로 진단 영역의 폭을 넓히고 있다. 소화기 분야에서는 가장 먼저 위내시경 사진을 분석하여 조기 위암을 발견하고 종양의 침범 깊이를 예측하는 AI 모델과[1], 대장내시경 사진을 분석해 대장 용종을 진단하는 시스템이 개발되었으며[2], 이미 일부 국가에서는 상품화가 되고 있다. 본고에서는 췌장담도 질환에서 AI가 어떻게 연구가 되고 있는지, 몇 가지 연구 결과를 통해 알아보고자 한다.
본론
1. 췌장 질환에서 AI 응용
1) 췌장낭종
Springer (Johns Hopkins University) 연구팀에서 췌장 낭종으로 수술은 받은 환자 436명의 데이터를 수집하여 지도학습(supervised learning) 방식으로 AI ‘컴프시스트 (CompCyst)’를 훈련시켰다[2]. 이 방법은 multivariate organization of combined alterations (MOCA) 알고리즘을 이용하여 임상 양상, 영상 검사, 낭종의 단백질 분석, DNA 돌연변이, 염색체 변이들의 정보 분석방법을 학습시켰다. 이후 AI 진단법 컴프시스트로 다른 췌장 낭종 환자 426명을 대상으로 퇴원해야 하는 환자(양성), 경과 관찰이 필요한 환자, 수술해야 하는 환자 3단계로 분류하였다.
표준 진단법에서는 퇴원(양성) 환자 진단 정확도가 18.9%에 불과하였지만, 컴프시스트는 60.4%에 달하였다. 또한 표준 진단법에 비해 컴프시스트에서 경과 관찰이 필요한 환자는 34.3%에서 48.6%로, 수술해야 하는 환자는 88.8%에서 90.8%로 진단 정확성이 향상되었다(Fig. 1). 컴프시스트는 기존 진단법을 보완하는 개념으로 불필요한 수술을 줄일 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
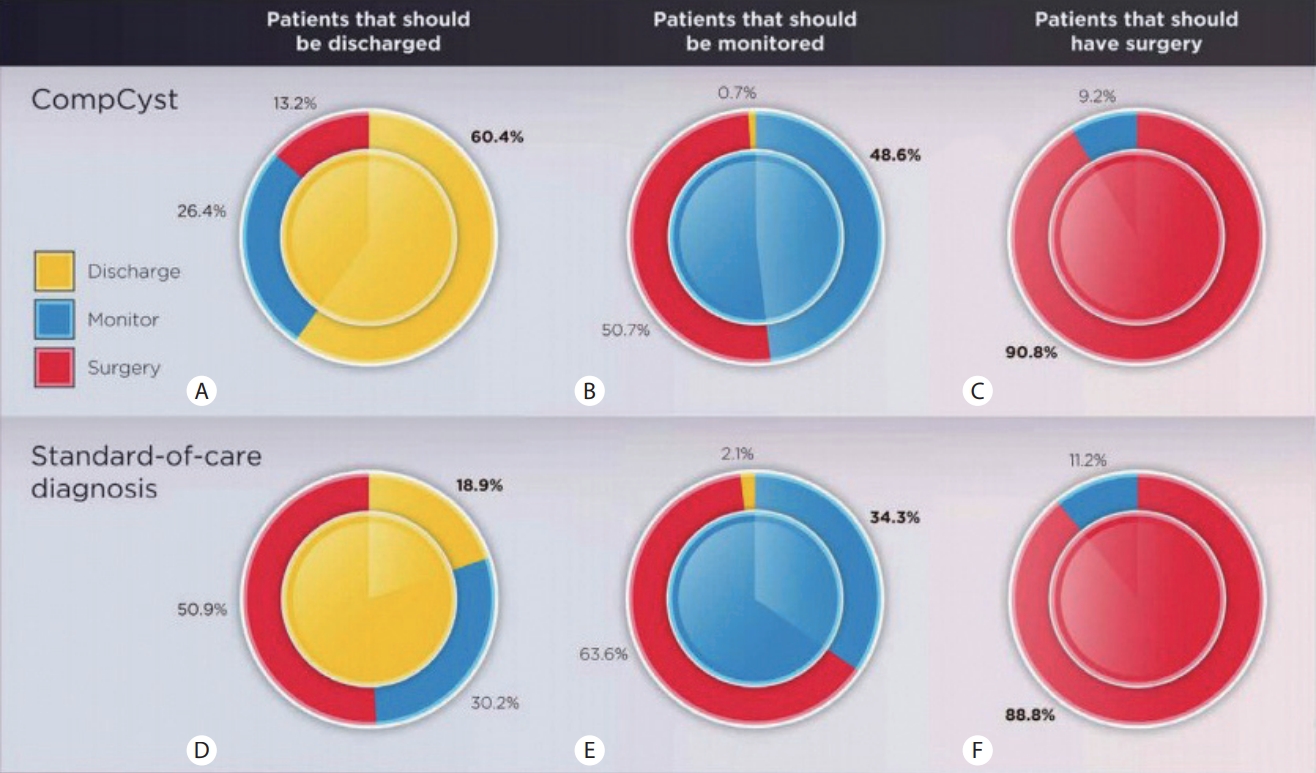
Management of pancreatic cysts. These donut charts show the management recommendations based on compcyst and standard of care compared with the gold standard, pathology. The center of the circle indicates the management recommendation based on the final surgical pathology classification. A fully solid circle—one where the inner and outer circles are fully the same color—would indicate 100% accuracy. The performance of compcyst compared with surgical pathology for cysts in whom the correct management was discharge, monitoring, or surgery is shown in (A), (B), or (c), respectively. The performance of standard of care compared with surgical pathology is shown in (d), (e), or (f), respectively (reprinted from Springer et al.[2]).
2) 췌장암
췌장암 분야에서는 조기 진단을 위한 목적으로 AI 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다. Fishman (Johns Hopkins University) 연구팀은 computed tomography (CT) radiomics를 기반으로 정상 췌장(정상 췌장과 췌장염)으로부터 췌장암을 구분하는 머신 러닝(machine learning) 알고리즘을 개발하였다[3]. 영상과 병리 데이터베이스를 이용하여, 췌장암으로 수술 받은 190명의 환자와 신장을 공여한 190명의 정상인의 CT 결과를 이용하여 478개의 radiomics 특징을 추출하였다. 이를 이용하여 학습 및 검증 과정을 거쳐 99.2% 정확도로 췌장암을 진단하였다(Fig. 2).

A 68-year-old man with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from our institution. (A) Axial cT image. (B) Pancreatic tumor region is outlined and shaded in red, and background pancreas region is outlined and shaded in yellow.
비슷한 연구가 대만에서 진행되었고 Liu (National Taiwan University Hospital) 연구팀에서는 370명의 췌장암 CT 사진과 대조군 256명의 CT 사진을 이용하여 합성곱신경망(convolutional neural network, CNN) 학습을 시행하였다[4]. CNN을 이용하여 췌장암 진단에 있어 99%의 정확도를 보였고 2 cm 이하의 작은 췌장암도 92.1% 진단 민감도를 보여주었다. CNN은 176명의 췌장암 환자에서 3명(1.7%)을 놓친 반면 영상의학과 의사는 168명의 췌장암 환자에서 12명(7%)을 놓쳤다.
또 다른 연구에서 Muhammad (Yale University) 연구팀은 환자의 정보를 이용하여 인공신경망(artificial neural network, ANN)을 통한 췌장암 고위험 환자의 예측 모델을 개발하였다[5]. ANN을 이용하여 환자의 정보를 학습시키고 검증을 반복한 뒤, 두 개의 데이터베이스를 통해 얻은 800,114명의 데이터에서 898명의 췌장암을 진단하는 과정을 거쳤다. 이 ANN 모델을 통해 87.3%의 민감도와 80.8%의 특이도로 췌장암 고위험 환자를 찾았다.
2. 담도 질환에서 AI 응용
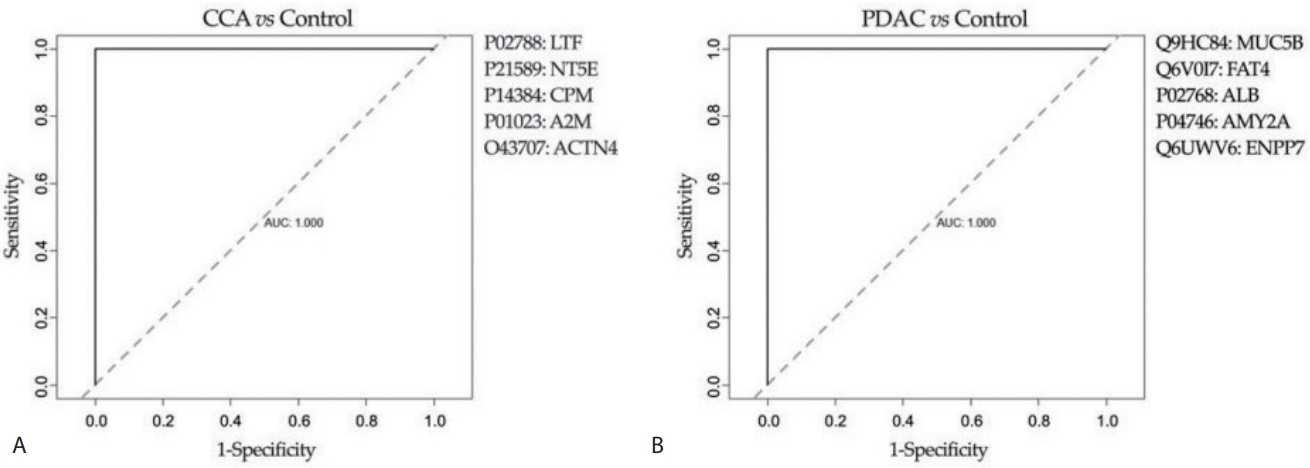
Avila (University of Navara Clinic) 연구팀은 담관 협착이 있는 환자에서 양성 협착과 악성 협착을 구분하기 위해, 담즙을 이용하여 대사체 물질(metabolomics)과 단백질 유전 정보(proteomics)를 질량분석법(mass spectrometry)과 핵자기 공명법(nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy)을 이용하여 분석하였다[6]. 내시경역행담췌관조영술을 통해 얻은 담즙을 이용하여 답즙의 구성물, 대사체 물질과 단백질 유전 정보를 이용한 바이오마커 등을 모두 분석하였고, 이를 머신 러닝을 이용하여 학습하였다. 학습 후 실제 데이터에서 검증하였고 뉴럴 네트워크를 통해 악성 질환과 양성 질환을 구분할 수 있는 지질(10가지) 및 단백질(5가지)의 패널을 확인하였다. 이 바이오마커를 이용하여 담도암과 췌장암 각각에서 양성 협착과 비교하였을 때 암 예측률이 모두 높게 나왔다(Fig. 3).
담도암은 발생하는 위치와 특성상 AI 연구에 어려움이 크고 아직까지 연구 결과가 적은 상태이다. Matake (Kyushu University) 연구팀에서는 간에 생기는 덩어리를 CT로 감별하기 위한 ANN 연구를 진행하였다[7]. 간암, 간내 담도암, 혈관종, 간 전이 환자를 각각 30명씩 등록하여 9개의 임상변수와 24개의 CT 특징을 이용하여 단층 피드-포워드 신경회로망(single three-layer feed forward ANN)과 오차역전파(back propagation) 알고리즘을 통해 학습하였다. 연구에 참여하지 않은 7명의 영상의학과 의사를 대상으로 120개의 같은 CT 사진을 보여주었고, 1차 판독에서는 0.888의 진단 정확도를 기록하였고 ANN 결과를 도움 받은 2차 판독에서는 0.934까지 진단 정확도가 증가하였다.
결론
췌장 질환과 담도 질환에서 질병을 예측하고 진단하기 위한 AI 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다. 특히, 췌장암과 담도암의 경우 조기 진단이 어렵고 5년 생존율이 매우 낮기 때문에 이와 같은 연구의 중요성은 매우 높아졌다. 국내에서도 AI 연구에 대한 관심이 매우 높아지고 있으며, 최근 국책사업으로 다기관 췌장담낭암 영상진단 인공지능 학습용 데이터 구축 사업이 진행되고 있어, 이를 활용한 추가적인 국내 AI 연구의 활성화가 기대된다.