췌장의 파골세포양 거대세포 미분화 암종 1예
Undifferentiated Pancreatic Carcinoma with Osteoclast-like Giant Cells: A Case Report
Article information
Abstract
파골세포양 거대세포형 미분화 암종은 췌장암의 1%만을 차지하는 흔치 않은 암종으로 알려져 있다. 저자들은 39세 남자에게서 진단된, 수술 및 항암치료를 시행한 1예를 소개하고자 한다.
Trans Abstract
Undifferentiated pancreatic carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells (UC-OGC) is uncommon, accounting for only 1% of all pancreatic carcinomas. We report a case of a 39-year-old man with undifferentiated pancreatic carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells who underwent successful surgical resection and chemotherapy.
INTRODUCTION
Undifferentiated pancreatic carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells (UC-OGC) has histologic and clinical characteristics that distinguish it from other undifferentiated carcinomas of the pancreas [1]. UC-OGC was first reported by Sommers and Meissner [2] in 1954 as an “unusual carcinoma.” This was followed by two cases reported in 1968 describing the similarities between giant cells of the carcinoma and osteoclasts of the bones [3]. Many case reports have reported controversial and differing prognoses of the disease [4-6]. When present without other epithelial neoplasms, pure UC-OGC is associated with a significantly better prognosis [7]. However, some reported a worse prognosis than those with pancreatic invasive ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) due to the large size and poor resectability of UC-OGC [8]. With the development of oncogenetics, UC-OGC cells have been found to originate from intraductal epithelial precursors [8], with high genetic similarity to conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas, and the World Health Organization has classified it as a distinct group since 2010 [1]. In this report, we present a case of a large undifferentiated carcinoma in a male patient who underwent pancreatoduodenectomy and right hemicolectomy with ongoing chemotherapy for UC-OGC.
CASE
A 39-year-old male was referred to our facility with pain in the right upper quadrant that had begun three days prior, and a mass in the same region. He was aware of a small palpable abdominal mass eight months prior and had noticed that the mass had increased in size. His abdomen was soft and flat, and physical examination at presentation did not reveal any tenderness. He had no other medical or family history except for hypertension. His blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and body temperature were 134/94 mmHg, 82 beats/min, 20 breaths/min, and 36.2℃, respectively. Initial laboratory tests were as follows: white blood cell count, 6,650/mm3 (normal range 4,000-10,000/mm3); hemoglobin, 12.5 g/dL (14.0-18.0 g/dL); platelet count, 312,000/mm3 (140,000-400,000/mm3); serum alanine aminotransferase, 11 IU/L (15-40 IU/L); aspartate aminotransferase, 10 IU/L (0-41 IU/L); amylase, 46 IU/L (20-104 IU/L); lipase, 32 IU/L (5.6-51.3 IU/L); C-reactive protein, 10.84 mg/dL (0.0-0.5 mg/dL); carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), 1.02 ng/mL (0-5 ng/mL); and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) 5.59 U/mL (0-37 U/mL).
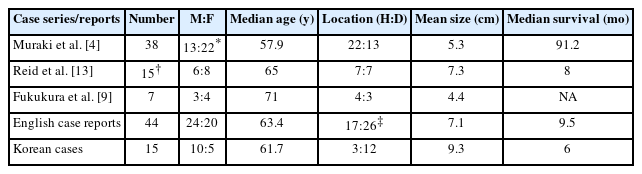
Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed an approximately 8-cm sized heterogeneously enhancing mass abutting the hepatic flexure colon, duodenum, and pancreatic head in the right upper abdomen. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showed the mass was embedded in the pancreatic head, suggesting a pancreatic origin with an intact mucosal layer compressing the colon. On T2 weighted images, the peripheral portion of the mass showed an encapsulated dark signal intensity with enhancement in the internal component, suggestive of a hemosiderin component. With heterogeneous cystic and hemorrhagic components, a pseudopapillary tumor arising from the pancreatic head was suspected (Fig. 1).
Cross-sectional images of the patient. (A) Initial contrast-enhanced abdominopelvic CT image shows heterogeneously enhancing mass of right upper abdomen. (B) Unenhanced T1 weighted MRI shows a high signal intensity at the peripheral rim of the tumor, suggesting hemorrhage from the tumor. (C) The enhanced T1 weighted image shows that the mass with infiltrative margin is embedded by the pancreas head, implying a pancreatic origin of the mass. (D) Inside the mass, multiple heterogenous enhancing lesions, suggestive of cystic and hemorrhagic components, were observed. CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
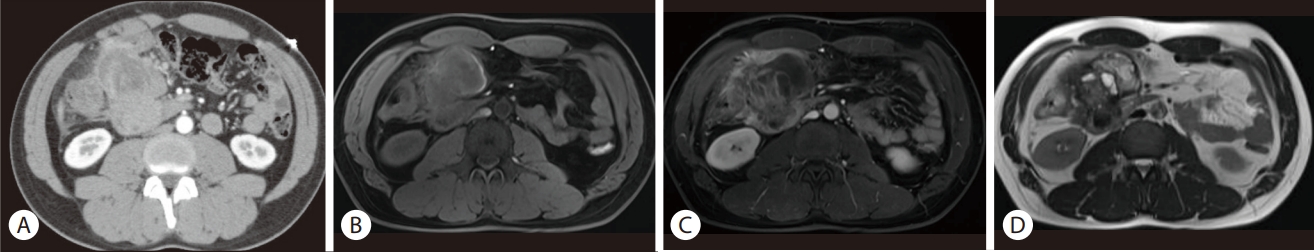
A malignant pancreatic mass was suspected, and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) and biopsy were performed. EUS-FNA revealed an 8-cm mass with heterogeneous echogenicity and multiple small cysts (Fig. 2). Macroscopic evaluation of the acquired tissue revealed old blood was noted with some whitish tissue cores. Cytology and biopsy specimens showed atypical mononuclear cells and multinucleated giant cells with an increased Ki-67 index (20-30%), which suggested malignancy.
Endoscopic ultrasound was performed using the balloon contact method. An 8-cm intra-abdominal mass with heterogeneous echogenicity was observed. The margins were relatively clear, with multiple small cysts inside the mass.
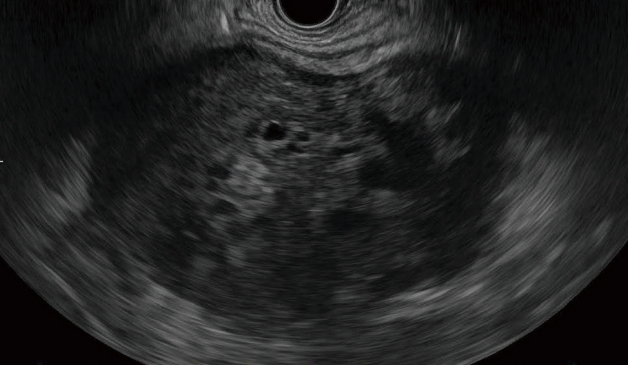
With laparotomy, a 9-cm sized mass originating from the pancreatic head was identified. The large mass was inseparable from the hepatic flexure of the colon, necessitating en bloc right colectomy and ileocolostomy (Fig. 3A). Pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy was performed (Fig. 3B), and the patient was discharged on postoperative day 12 without any surgical complications.
Intraoperative findings and specimens. (A) A 9-cm tumor originating from the pancreatic head. The hepatic flexure and mesocolon were adherent to the tumor, necessitating a combined right hemicolectomy. (B) Photograph of the bisected specimen. (C) The cut surface of the mass was heterogeneously solid and cystic, filled with hemorrhagic materials. SMV, superior mesenteric vein.
The cut surface of the mass was heterogeneously solid and cystic, and filled with hemorrhagic material (Fig. 3C). Microscopic examination revealed three types of cells (mononuclear neoplastic cells, histiocytes, and osteoclast-like giant cells) with hemorrhage and necrosis. No common pancreatic adenocarcinomas were observed. On immunohistochemical stains, cytokeratin was negative, CD68 was positive for histiocytes and osteoclast-like giant cells (Fig. 4).
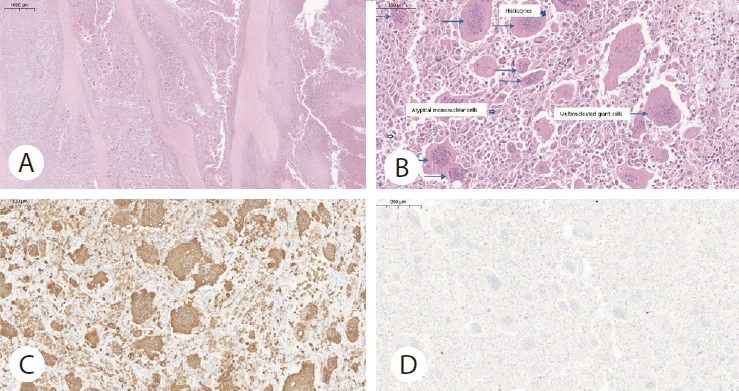
Representative histologic features of undifferentiated pancreatic carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells. (A) Tumor-infiltrating fibrotic tissue and hemorrhagic necrosis (Hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×20). (B) The tumor is composed of mononuclear atypical cells (arrowheads with filled inside), histiocytes (Hollow arrowheads), and multinucleated osteoclast-like giant cells (blue arrows) (Hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×300). (C) Immunohistochemical staining for CD68 showed the scattered histiocytes and multinucleated osteoclast-like giant cells (×200). (D) Negative pan-cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining (Cytokeratin, ×200)
Based on the histologic findings mentioned above, the mass was diagnosed as an undifferentiated carcinoma of the pancreas with osteoclast-like giant cells.
The disease stage was pT3 (bowel invasion)N0(0/14)M0, and pStage IIA was diagnosed. Postoperatively, the patient underwent adjuvant FOLFIRINOX (oxaliplatin, irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin) chemotherapy for 12 months without evidence of recurrence. During surveillance studies, multiple liver and paranephric metastases developed, and he underwent gemcitabine/nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel chemotherapy for three months.
DISCCUSION
UC-OGC is a rare type of pancreatic cancer, and our case appears to be 15th domestic case reported according to searches of the Research Information Sharing Service (RISS) and PubMed (Table 1). Once considered a subtype of anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas with a poor prognosis, it was reclassified as an independent type with its distinct histologic and prognostic features in 2010 [1]. UC-OGC consists of three cell types: mononuclear histiocytes expressing CD163, highly pleomorphic and atypical mononuclear neoplastic cells with enlarged nuclei, and large osteoclast-like giant cells with phagocytic activity [1].
An extensive review of UC-OGC cases reported in the English literature over the last decade was performed by searching PubMed using the keywords “pancreas carcinoma,” and “osteoclast like giant cells,” and revealed a total of 44 case reports (Supplementary Table 1). The characteristics of the diagnosed patients from those case reports, together with those from two other studies, are summarized in Table 1.
Over the last 10 years, in the reported UC-OGC case reports and case series written in English, the average age was 62.2 years (range 29-86 y, median 66 y) and the male-to-female ratio was 46:54. UC-OGC has a slight female predominance, and most cases present with a tumor size of >5 cm [8]. The characteristics of these patients were similar to those of a recent multicenter study, which showed female predominance and a mean age of 58 years [4]. A total of 20, 24, and 25 cases each reported tumor locations of the head, body, and tail, respectively, including large and multiple locations.
The typical clinical manifestations of UC-OGC, including abdominal pain, weight loss, nausea, and occasional jaundice and anemia, are similar to those of other pancreatic ductal carcinomas [4].
Radiologically, UC-OGC can show hypervascularity, reflecting its rapid growth, and a hyperdense solid or cystic mass with an ill-defined margin [5]. On both the T1 and T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of some reports, low signal intensity with relatively high central signal intensity may be seen in UC-OGC in response to hemosiderin deposits of histiocytes with central necrosis [8,9]. Nevertheless, distinguishing UC-OGC from unusual pancreatic tumors using imaging alone is difficult, so pathologic diagnosis is essential [8]. Serologically, UC-OGC was less strongly associated with elevated serum CEA and CA19-9 levels than PDAC [5].
The diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA for UC-OGC can be lower than that for other pancreatic malignancies because three types of distinctive origins must be identified for pathologic diagnosis [8,10]. Muraki reported that only one-third of cases were diagnosed as UC-OGC by preoperative biopsy such as EUS-FNA [4]. From the cases reported in English over the last ten years, 16 cases underwent EUS-FNA, and two cases underwent biopsy at the metastatic liver lesion [11,12]. Among the 16 cases that underwent EUS-FNA, 14 cases were suspected to be malignant, with eight cases suggestive of or diagnosed as UC-OGC. Although EUS-FNA seems to be safe for PDAC, there is a concern for pre-operative EUS-FNA for UC-OCCs [13]. However, the number of included patients were small and selection bias could have led to these results. Additionally, there could be distinctive biological properties of UC-OGCs [13]. Therefore, further studies should be conducted to ensure the safety of FNA in UC-OGC. Our patient underwent EUS-FNA, and tissue samples of osteoclast-like giant cells with spindle cells and extensive necrosis were acquired, suggesting UC-OGC.
With the development of immunohistochemistry and sequencing technologies, UC-OGC immunoreactivity has been tested, providing clues regarding the pathogenesis thereof. In most cases, mononuclear neoplastic cells were positive for vimentin, keratin, and p53 staining. In contrast, osteoclast-like giant cells were positive for CD68, vimentin, leukocyte common antigen, and keratin, but negative for p53 [4,8]. The histiocytic marker CD68 is expressed in osteoclastic cells, whereas pleomorphic/giant carcinoma cells express p53 and often lack cytokeratin [4]. In our case, IHC markers were tested on EUS-FNA sample for differential diagnosis, and P53 was positive for atypical mononuclear cells and osteoclast-like giant cells. Vimentin was positive for all cells, and CD68 was positive for histiocytes and osteoclast-like giant cells. Cytokeratin was negative. In the study by Luchini et al. [14], pathologic samples of UC-OGC were immunostained for the PD-1, PD-L1, and CD163 receptors, and showed a high probability of PD-L1 receptor expression in neoplastic cells and a higher frequency of PD-L1 expression in mixed cases of UC-OGC with PDAC, which was accompanied by a significant (up to 3-fold) increase in mortality [4,7].
In terms of prognosis, contradictory reports exist. One study reported better prognosis of pure UC-OGC than that of PDAC [4], particularly after complete resection [6]. The patient in our case was alive for more than 24 months after diagnosis, even with local invasion of the colon (pT3). In our summarized data, however, the median survival time was only 11 months (range: 3-120 months) (Table 1). The reason may be associated with mixture of PDAC with UC-OGC, leading to worse prognosis [6,7]. Without mixed adenocarcinoma confirmed by pathology, pure UC-OGC had a nearly twofold median survival, comparatively [7]. Kobayashi et al. asserted that older age, male sex, smaller tumor size, lymph node metastasis, and concomitant components of PDAC are markers indicating shorter survival [6].
Although the standard treatment for UC-OGC has yet to be established, surgical resection is considered the best treatment option for localized disease [8]. However, the efficacy of radiotherapy and chemotherapy for UC-OGC remains uncertain [5]. Because UC-OGC is considered a variant of PDAC [7], the chemotherapy regimen is the same as that for PDAC, and includes FOLFIRINOX and gemcitabine plus albumin-bound paclitaxel. Although no universally accepted guidelines exist, some case reports [4,11] have used adjuvant chemotherapy, with the same regimen of FOLFIRINOX as PDAC, and achieved a median survival of 91 months. In our case, disease-free survival of one year was obtained with 12 cycles of adjuvant FOLFIRINOX therapy. After recurrence, the patient achieved a partial response to second-line gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy and maintenance treatment.
In conclusions, undifferentiated pancreatic carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells is a rare and poorly understood carcinoma with limited treatment options. With the development of immunohistochemistry and oncogenetics, optimal treatment options for genetic characteristics may be identified.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
Hoonsub So is currently serving as an Editor in Editorial Board of the Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract; however, Hoonsub So was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this manuscript. Younghun Jeon, Jaheung Koo, Yang Won Nah, Hyunsoo Lim, Binnari Kim, Tae Young Lee, and Sung Jo Bang have no potential conflicts of interest.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary materials can be found via https://doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2023.28.4.120
Supplementary Table 1.
Case reports reporting UC-OGC in English literature from January 2014 to February 2023
Supplementary Table 2.
Reported cases of UC-OGCs in Korea